Automation Rules
Minimum version requirement: 1.2.0
Overview
Have you ever missed reducing power right at first crack because you were focused on listening to the beans? Or worried about your roaster overheating when you step away for a moment?
Automation rules solve these common roasting challenges by executing predefined actions automatically when specific conditions are met. Think of it as having an experienced roasting assistant who never gets distracted and always follows your instructions precisely.
Automation Rules vs Auto Roasting
Before diving into automation rules, let's clarify two easily confused concepts:
Auto Roasting
- Essence: Complete hands-off "curve replication" mode
- How it works: Strictly follows preset roasting profile time and temperature curves
- Analogy: Like a factory assembly line, following blueprints exactly with no human intervention
- Use case: Reproduce verified classic roasting profiles for consistency
Automation Rules
- Essence: Intelligent roasting assistant providing support during manual operation
- How it works: Triggers preset actions when specific conditions are met, but roaster maintains overall control
- Analogy: Like cruise control and lane assist in cars - assists driving but doesn't replace the driver
- Use case: Provides safety protection, operation reminders, and process assistance during manual roasting
Collaborative Design Philosophy
- Non-interference: Auto roasting hides automation rule entries to avoid accidentally disrupting precise curve replication
- Flexible choice: Pure manual, manual with automation assistance, or fully automatic roasting
- Safety first: Device-level automation rules always active for basic safety protection
Common Roasting Problems That Automation Solves
"I always forget to adjust power at the right temperature"
→ Set temperature triggers that automatically adjust heater power when beans reach specific temperatures.
"I'm worried about safety when roasting unattended"
→ Create safety rules that immediately shut down heating if temperatures exceed safe limits.
"I want to recreate that perfect roast from last week"
→ Record your successful roasting sequences as automation rules for consistent reproduction.
"I need to focus on cupping notes, not watching the timer"
→ Let automation handle routine adjustments while you concentrate on sensory evaluation.
System Architecture
WHEN-IF-DO Structure
Automation rules use a three-part logical structure:
- WHEN (Triggers): Conditions that activate the rule
- IF (Conditions): Additional criteria that must be met (optional)
- DO (Actions): Operations to execute when conditions are satisfied
Dual-Scope System
The automation system operates on two levels:
Global Automation
- Device-level rules that apply to all roasting profiles
- Persistent across all roasting sessions
- Suitable for safety rules and standard operations
Profile Automation
- Profile-specific rules for individual roasting profiles
- Customized for specific beans or roasting styles
- Override or supplement global rules
Both scopes run independently during roasting, with the system coordinating device control to prevent conflicts.
Automation Feature Entry and Interface Guide
How to Access Automation Settings
The main entry point for automation features is located on the Prepare Roasting page, but is only displayed in manual mode:
Automation Entry in Manual Mode
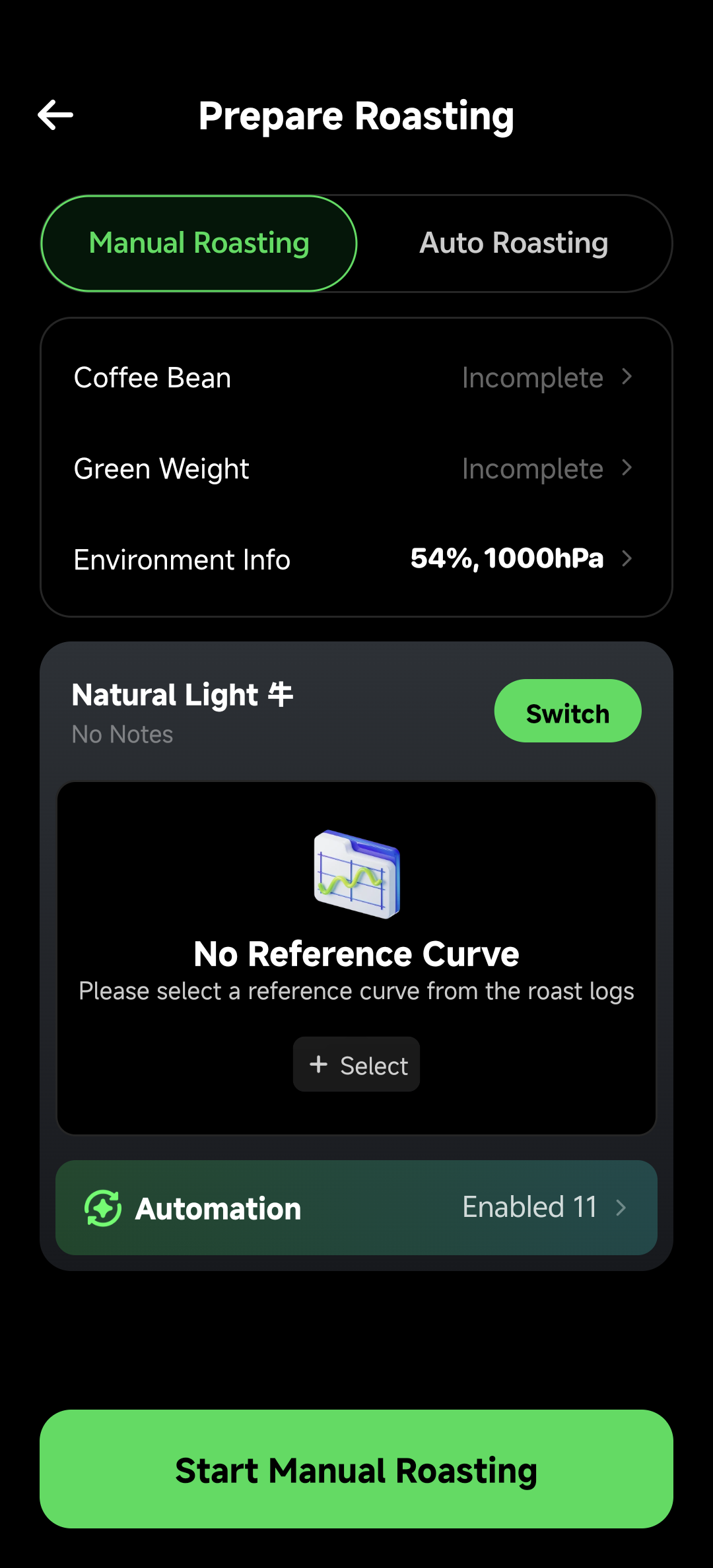
In manual roasting mode, you can see:
- Automation Entry: Green "Automation Enabled 11" button at the bottom
- Rule Count: Shows the number of currently enabled automation rules
- Quick Access: One-click entry to automation settings page
Interface Changes in Auto Mode
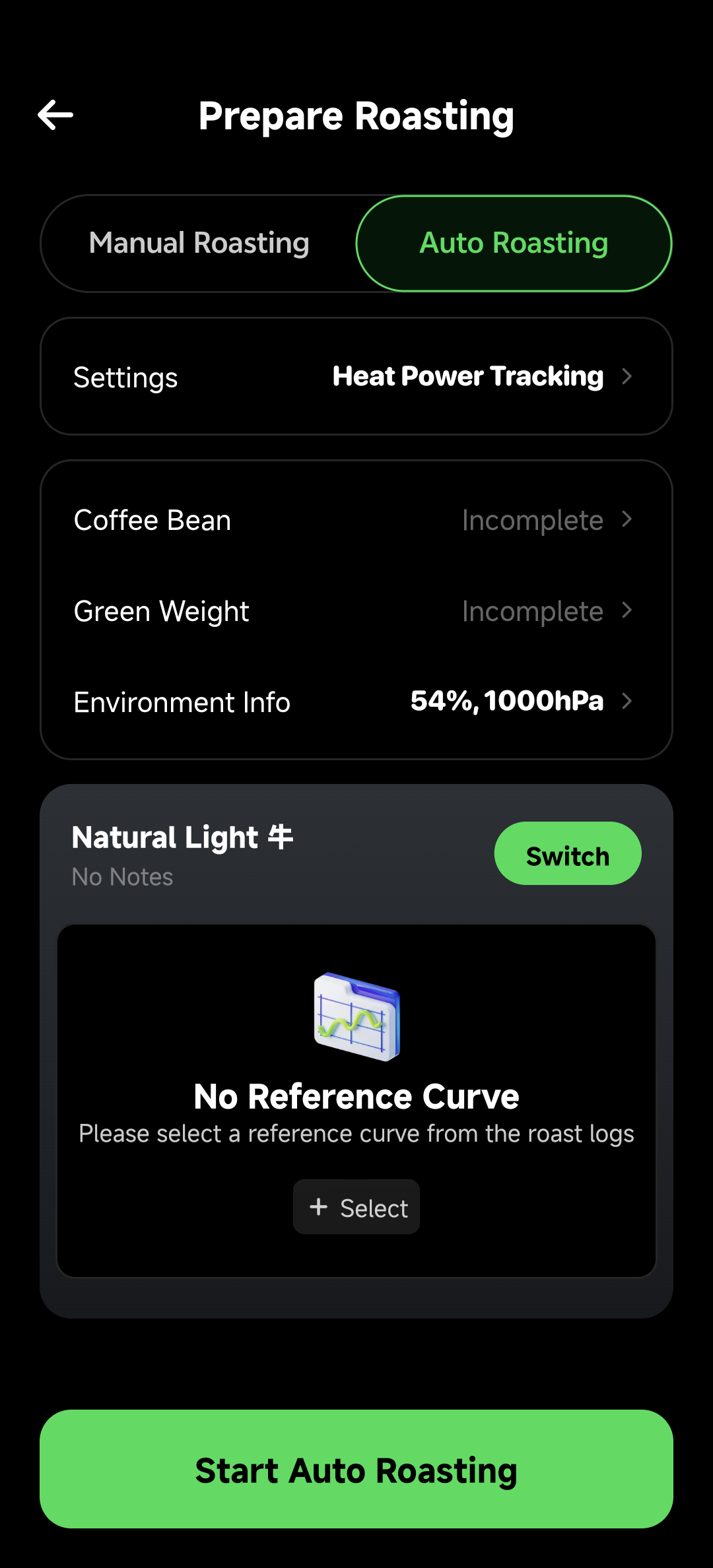
In auto roasting mode:
- Hidden Automation Entry: Prevents accidental interference with precise curve replication
- Auto Roasting Settings: Shows dedicated configurations like "Heat Power Tracking"
- Mode Switching: Can switch between manual/auto modes at any time
Automation Settings Interface
Main Interface Layout
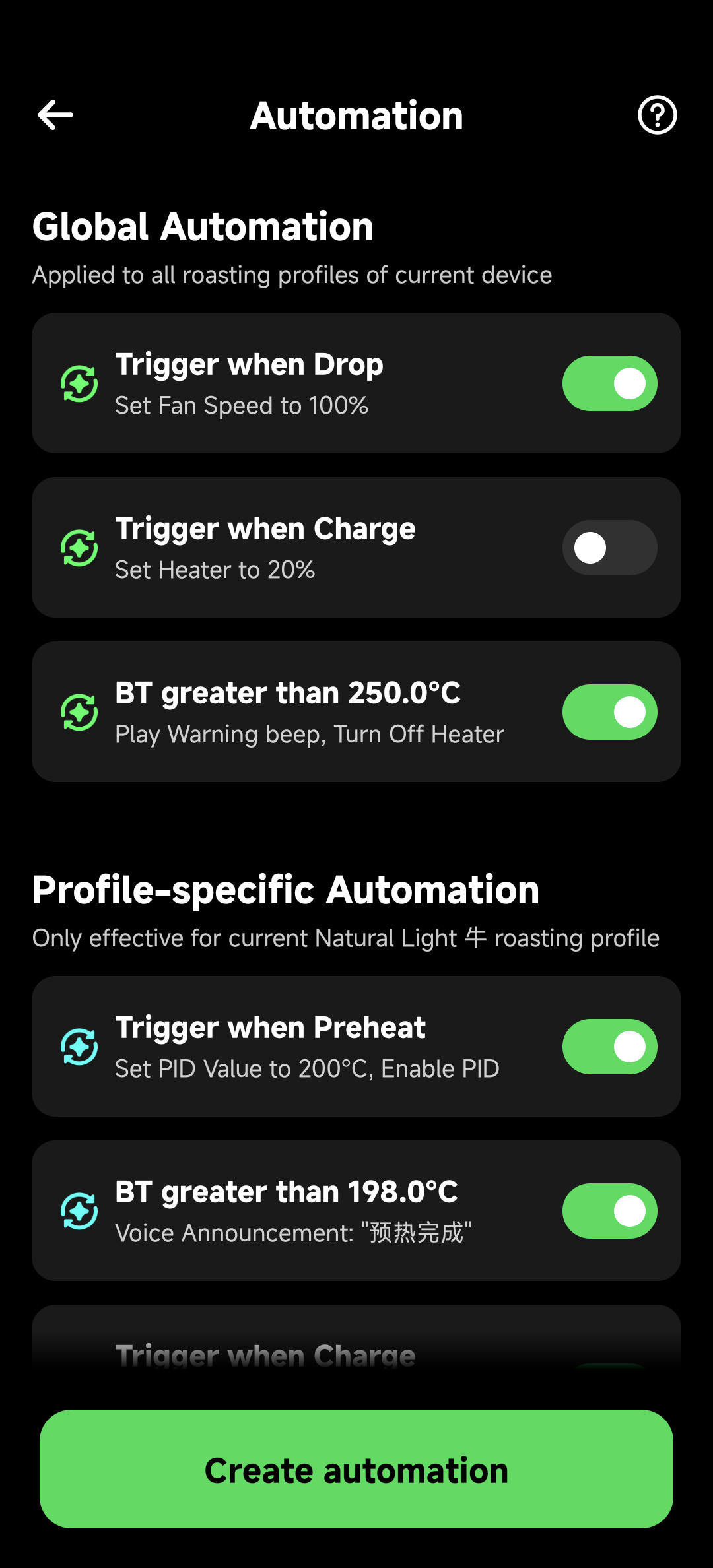
The automation settings interface uses a clear dual-layer architecture:
Global Automation Section:
- Orange Icons: Indicates device-level universal rules
- Scope Description: "Applied to all roasting profiles of current device"
- Safety Rules: Such as 100% fan on drop, over-temperature protection, etc.
Profile-specific Automation Section:
- Green Icons: Indicates profile-specific rules
- Scope Description: "Only effective for current [profile name] roasting profile"
- Process Rules: Such as preheat PID settings, temperature voice reminders, etc.
Rule List Details
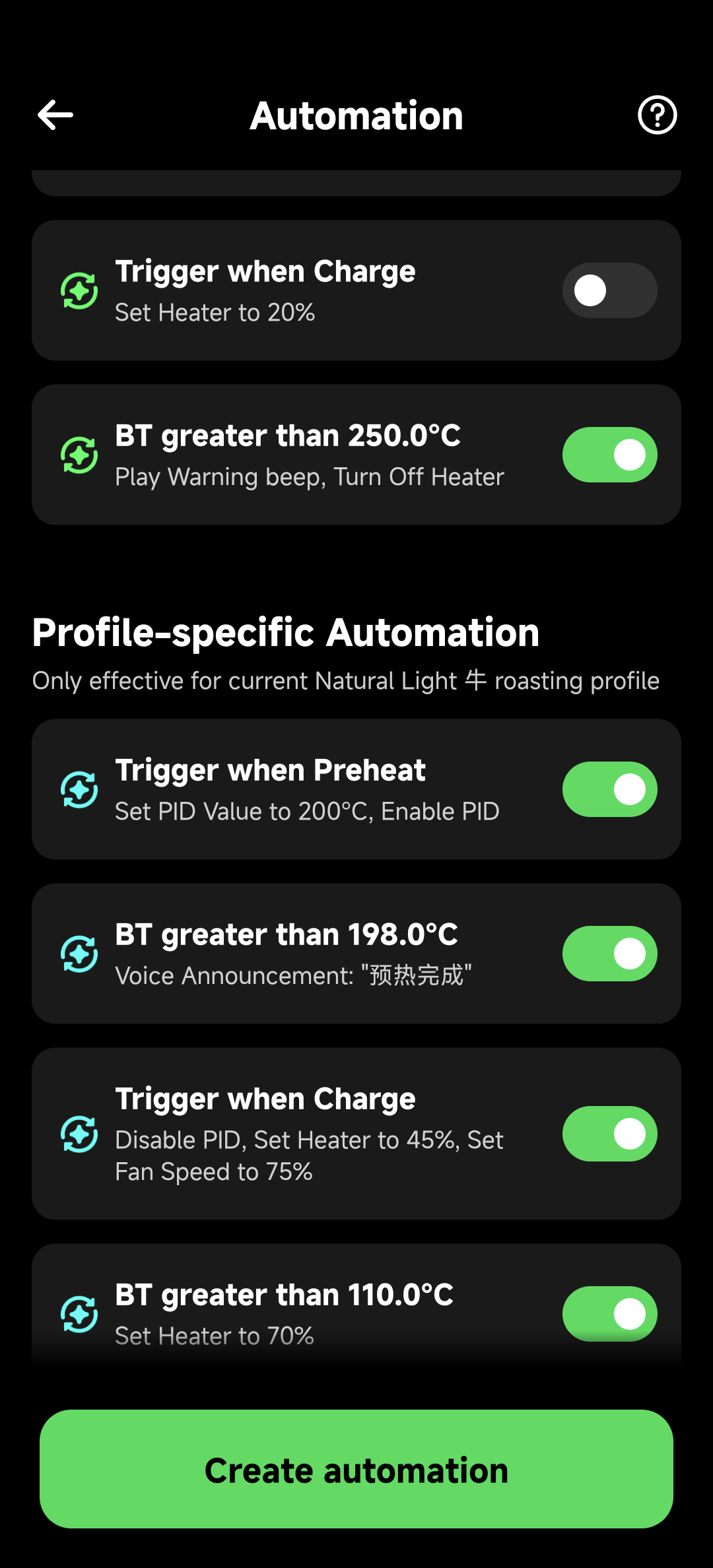
Each rule card contains:
- Rule Description: Natural language description of trigger conditions and actions
- Toggle Control: Right-side slider to enable/disable rules
- Status Indicator: Green = enabled, gray = disabled
Rule Edit Interface
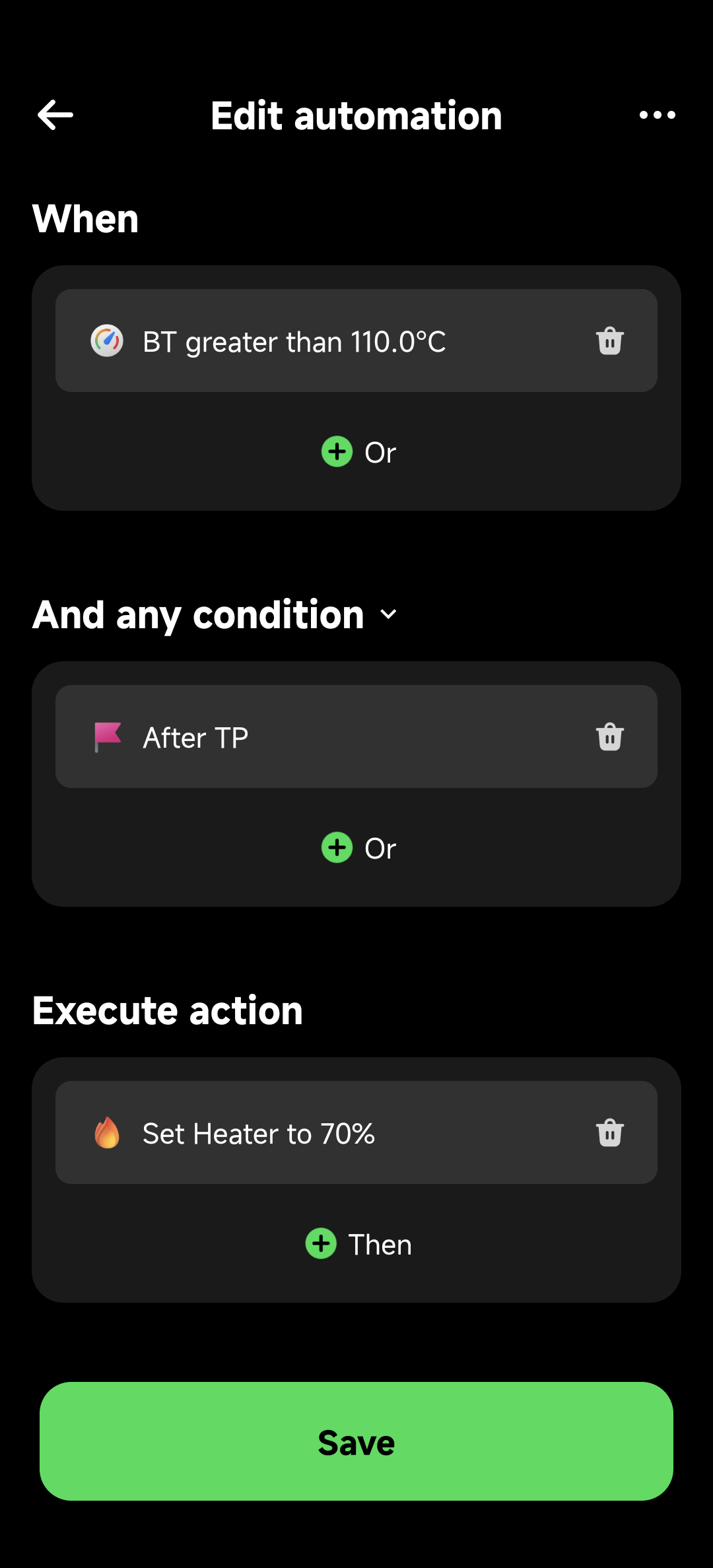
Visual editing of WHEN-IF-DO structure:
- WHEN (Triggers): Such as "BT greater than 110.0°C"
- IF (Conditions): Such as "After TP" (after turning point)
- DO (Actions): Such as "Set Heater to 70%"
- Logic Combinations: "Or" and "Then" buttons to add more conditions and actions
Triggers
Triggers define when automation rules activate.
Event Triggers
Monitor roasting stage events:
- Preheat Complete, Charge, Turning Point
- First Crack, Second Crack, Drop
- Smart event history tracking prevents duplicate activations
Temperature Triggers
Monitor temperature values:
- Bean Temperature (BT) and Environment Temperature (ET)
- Multi-unit support: Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin with automatic conversion
- Comparison operators: Greater than, less than, equal to
- Smart tolerance: Prevents false triggers from sensor noise
Time Triggers
Monitor roasting duration:
- Second-level precision timing
- All comparison operations supported
- Built-in tolerance handling (±5 seconds)
Multiple Trigger Logic
Rules can have multiple triggers with OR logic - any trigger activation executes the rule.
Conditions
Conditions provide additional criteria that must be met after trigger activation.
Event State Conditions
- Before Event: Execute before specific events occur
- After Event: Execute after specific events complete
- During Event: Execute while events are active
Temperature Conditions
- Support for BT and ET monitoring
- Multi-unit system with automatic conversion
- Smart tolerance handling
Time Conditions
- Precise time detection with second-level accuracy
- Flexible comparison operations
- Tolerance mechanism prevents false triggers
Logic Options
- AND Logic: All conditions must be satisfied
- OR Logic: Any condition satisfaction triggers execution
- Interface allows dynamic logic switching
Actions
Actions define operations to perform when rule conditions are met.
Device Control Actions
- Heater Control: Power adjustment or on/off control
- Fan Control: Speed adjustment or on/off control
- Drum Control: Speed adjustment (drum roasters)
- Cooling Fan Control: Cooling system on/off
PID Control Actions
- Set Target Temperature: Precise temperature control
- Auto Heating Toggle: Enable/disable automatic heating
- Parameter Adjustment: Configure Kp, Ki, Kd parameters
Notification Actions
- Voice Announcements: TTS text-to-speech with custom messages
- Alert Sounds: Success, warning, info sound effects
- Automatic Fallback: TTS backup when audio playback fails
Flow Control Actions
- Delay Action: Non-blocking time delays
- Action Sequences: Multiple actions executed in order
Device Compatibility
The system automatically detects device capabilities and displays only supported action types.
Creating Automation Rules
Example: Smart Power Reduction
Goal: "When first crack starts OR bean temperature exceeds 205°C, if roasting time exceeds 8 minutes, wait 30 seconds then reduce power to 60% and announce completion"
Step 1: Access Automation Settings
- Navigate to automation settings using entry points described above
- Select "Global Automation" or "Profile Automation"
- Click "+" or "Add New Rule"
Step 2: Configure Triggers (WHEN)
- Add Event Trigger: First Crack
- Add Temperature Trigger: BT > 205°C
- Set trigger logic to OR
Step 3: Configure Conditions (IF)
- Add Time Condition: Roast Time > 8:00
- Keep condition logic as AND
Step 4: Configure Actions (DO)
- Add Delay Action: 30 seconds
- Add Set Heater Action: 60%
- Add Voice Announcement: "Power reduction complete"
Step 5: Save and Test
- Name the rule: "Smart Power Reduction"
- Save and activate
- Test during next roasting session
Global Automation Management
Global automation provides device-level rule management for universal operations.
Device-Level Persistence
- Rules stored using device-specific templates
- Persistent across application restarts
- Automatic application to new profiles
Access and Management
- Available through device settings page
- Independent rule creation and editing
- Applies to all roasting profiles for the device
Use Cases
- Safety Rules: Over-temperature protection, emergency shutdown
- Standard Operations: Charge procedures, basic power adjustments
- Universal Notifications: Stage announcements, audio alerts
Best Practices
Global Automation Suitable For:
- Safety and monitoring rules
- Standard operational procedures
- Universal notifications and alerts
Profile Automation Suitable For:
- Bean-specific temperature and timing controls
- Specialized processing techniques
- Experimental roasting methods
Benefits
- Efficiency: Set once, apply to all profiles
- Safety: Centralized critical rule management
- Consistency: Core roasting principles applied universally
- Flexibility: Parallel operation with profile-specific rules
Use Cases and Applications
Core Positioning of Automation Rules
The automation rules system is designed specifically for manual roasting assistance, with the core concept being "program your own roasting assistant." Through carefully designed rule combinations, you can create an intelligent assistance system that approaches the effectiveness of fully automatic roasting.
Complementary Relationship with Auto Roasting
- Auto Roasting: Suitable for reproducing verified classic profiles, pursuing precise replication
- Automation Rules: Suitable for exploring new processes, personalized adjustments, and safety protection
- Collaborative Use: Use automation rules to explore and validate new roasting approaches, then create successful approaches as auto roasting profiles
1. Intelligent Roasting Assistant (Recommended for Beginners)
By combining multiple automation rules, you can create an intelligent roasting assistant system that provides precise operational support at critical moments.
Case Study: Light Roast Coffee Intelligent Assistance System
Goal: Create a set of intelligent assistance rules for light roast coffee, ensuring precise control at key nodes
Rule Combination:
- Safe Preheating: Set PID to 200°C when preheat completes, ensuring stable charge temperature
- Standard Charge: Automatically set 65% power, 65% fan at charge for stable initial conditions
- Progressive Power Reduction:
- 111°C → 70% power (late drying adjustment)
- 122°C → 65% power (Maillard reaction period)
- 132°C → 60% power (pre-first crack preparation)
- Precise Finishing: 172°C → 50% power, 80% fan (development optimization)
- Completion Reminder: 192°C → voice notification "suggest drop"
Advantages:
- Learning Tool: Beginners can observe the effects and timing of each adjustment
- Consistency: Ensures the same key operations are executed in every roast
- Flexibility: Roaster can still manually intervene and adjust at any time
- Safety: Built-in temperature and time protection mechanisms
2. Safety and Protection Systems
Over-Temperature Protection
WHEN: Bean Temperature > 230°C
DO: Set Heater to 0%, Voice Alert "Over-temperature detected"Emergency Shutdown
WHEN: Environment Temperature > 250°C
DO: Set Heater to 0%, Set Fan to 100%, Emergency Audio AlertRoasting Time Limits
WHEN: Roast Time > 15 minutes
IF: No Drop Event Recorded
DO: Voice Warning "Extended roasting time detected"3. Operational Assistance
Standard Charge Procedure
WHEN: Charge Event
DO: Set Heater to 80%, Set Fan to 70%, Voice "Charge complete"First Crack Management
WHEN: First Crack Event
DO: Reduce Heater by 20%, Voice "First crack detected"Development Time Tracking
WHEN: First Crack Event
DO: Start Development Timer, Voice "Development phase started"4. Learning and Training
Guided Roasting for Beginners
- Automated voice prompts at key roasting stages
- Standard power adjustments for common roasting profiles
- Temperature-based guidance: "Approaching first crack temperature"
Advanced Technique Practice
- Pre-configured sequences for specific roasting styles
- Automated execution of complex roasting curves
- Consistent parameter changes for comparative learning
5. Quality Consistency
Commercial Roasting Standards
- Automated reproduction of established roasting profiles
- Consistent timing and temperature control
- Elimination of operator variation in routine operations
Batch-to-Batch Consistency
- Identical automation sequences for production roasting
- Standardized safety and quality checkpoints
- Reduced variability in final product characteristics
6. Experimental and Development Work
A/B Testing
- Automated variations in roasting parameters
- Consistent execution of experimental protocols
- Precise control of single variables
Recipe Development
- Systematic exploration of roasting parameter combinations
- Automated documentation of successful sequences
- Rapid iteration through profile variations
7. Specialized Applications
PID-Controlled Precision Roasting
WHEN: Preheat Event
DO: Set PID Target 200°C, Enable Auto Heating
WHEN: Charge Event
DO: Disable PID, Switch to Manual ControlMulti-Stage Roasting Profiles
WHEN: Bean Temperature 120°C
DO: Set Power 70%, Set Fan 60%
WHEN: Bean Temperature 160°C
DO: Set Power 50%, Set Fan 80%
WHEN: Bean Temperature 190°C
DO: Set Power 30%, Voice "Approaching finish"Getting Started with Automation
Beginner Approach
- Start with safety rules (over-temperature protection)
- Add basic operational assistance (charge procedures)
- Implement voice notifications for key events
- Gradually add more complex automation sequences
Advanced Implementation
- Study manufacturer-provided automation profiles
- Adapt proven sequences to your specific requirements
- Create bean-specific automation profiles
- Develop comprehensive safety and quality systems
Best Practices
- Always include safety rules in global automation
- Test new automation sequences with practice roasts
- Monitor automation performance and adjust as needed
- Maintain manual override capability for all automated functions
Summary and Future Outlook
Core Value of Automation Rules
HiBean's automation rules system represents a significant advancement in coffee roasting technology, perfectly balancing automation consistency with manual roasting flexibility:
Technical Innovation
- WHEN-IF-DO Declarative Rules: Makes complex logic intuitive and understandable
- Dual-Layer Architecture Design: Device-level safety protection + profile-level process optimization
- Intelligent Device Adaptation: Dynamic feature detection based on Cluster capabilities
- Seamless Temperature Unit Conversion: Globalized user experience
Roasting Value
- Lower Learning Curve: Beginners can quickly get started with expert-level rules
- Enhanced Consistency: Eliminates random errors from manual operations
- Increased Safety: 24/7 device monitoring and protection
- Stimulates Creativity: Frees roasters from mechanical operations to focus on sensory judgment and process innovation
Future Possibilities
- AI-Assisted Rule Generation: Automatically generate optimized rules based on historical data
- Community Rule Sharing: Rule exchange and collaboration between roasters
- Device Learning Capabilities: Automatic rule parameter adjustment based on roasting results
- Multi-Device Coordination: Rule synchronization and adaptation between different devices
Begin Your Automated Roasting Journey
Whether you're a beginner or experienced roaster, automation rules can bring a completely new experience to your roasting:
- Start with Safety Rules: Establish a basic device protection system
- Add Operational Assistance: Make routine operations more precise and consistent
- Explore Process Innovation: Use automation rules to validate new roasting concepts
- Share and Learn: Exchange successful rule configurations with the roasting community
Automation rules are not meant to replace the roaster's skills, but to become your most capable assistant, helping every roast achieve the perfect results you pursue.
